|
|
@@ -1,186 +0,0 @@
|
|
|
-======================================
|
|
|
-Customizing the Django admin interface
|
|
|
-======================================
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. warning::
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- The design of the admin has changed somewhat since this document was
|
|
|
- written, and parts may not apply any more. This document is no longer
|
|
|
- maintained since an official API for customizing the Django admin interface
|
|
|
- is in development.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Django's dynamic admin interface gives you a fully-functional admin for free
|
|
|
-with no hand-coding required. The dynamic admin is designed to be
|
|
|
-production-ready, not just a starting point, so you can use it as-is on a real
|
|
|
-site. While the underlying format of the admin pages is built in to Django, you
|
|
|
-can customize the look and feel by editing the admin stylesheet and images.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Here's a quick and dirty overview some of the main styles and classes used in
|
|
|
-the Django admin CSS.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Modules
|
|
|
-=======
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-The ``.module`` class is a basic building block for grouping content in the
|
|
|
-admin. It's generally applied to a ``div`` or a ``fieldset``. It wraps the content
|
|
|
-group in a box and applies certain styles to the elements within. An ``h2``
|
|
|
-within a ``div.module`` will align to the top of the ``div`` as a header for the
|
|
|
-whole group.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. image:: _images/module.png
|
|
|
- :alt: Example use of module class on admin homepage
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Column Types
|
|
|
-============
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. note::
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- All admin pages (except the dashboard) are fluid-width. All fixed-width
|
|
|
- classes from previous Django versions have been removed.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-The base template for each admin page has a block that defines the column
|
|
|
-structure for the page. This sets a class on the page content area
|
|
|
-(``div#content``) so everything on the page knows how wide it should be. There
|
|
|
-are three column types available.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-colM
|
|
|
- This is the default column setting for all pages. The "M" stands for "main".
|
|
|
- Assumes that all content on the page is in one main column
|
|
|
- (``div#content-main``).
|
|
|
-colMS
|
|
|
- This is for pages with one main column and a sidebar on the right. The "S"
|
|
|
- stands for "sidebar". Assumes that main content is in ``div#content-main``
|
|
|
- and sidebar content is in ``div#content-related``. This is used on the main
|
|
|
- admin page.
|
|
|
-colSM
|
|
|
- Same as above, with the sidebar on the left. The source order of the columns
|
|
|
- doesn't matter.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-For instance, you could stick this in a template to make a two-column page with
|
|
|
-the sidebar on the right:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. code-block:: html+django
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- {% block coltype %}colMS{% endblock %}
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Text Styles
|
|
|
-===========
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Font Sizes
|
|
|
-----------
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Most HTML elements (headers, lists, etc.) have base font sizes in the stylesheet
|
|
|
-based on context. There are three classes are available for forcing text to a
|
|
|
-certain size in any context.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-small
|
|
|
- 11px
|
|
|
-tiny
|
|
|
- 10px
|
|
|
-mini
|
|
|
- 9px (use sparingly)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Font Styles and Alignment
|
|
|
--------------------------
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-There are also a few styles for styling text.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.quiet
|
|
|
- Sets font color to light gray. Good for side notes in instructions. Combine
|
|
|
- with ``.small`` or ``.tiny`` for sheer excitement.
|
|
|
-.help
|
|
|
- This is a custom class for blocks of inline help text explaining the
|
|
|
- function of form elements. It makes text smaller and gray, and when applied
|
|
|
- to ``p`` elements within ``.form-row`` elements (see Form Styles below),
|
|
|
- it will offset the text to align with the form field. Use this for help
|
|
|
- text, instead of ``small quiet``. It works on other elements, but try to
|
|
|
- put the class on a ``p`` whenever you can.
|
|
|
-.align-left
|
|
|
- It aligns the text left. Only works on block elements containing inline
|
|
|
- elements.
|
|
|
-.align-right
|
|
|
- Are you paying attention?
|
|
|
-.nowrap
|
|
|
- Keeps text and inline objects from wrapping. Comes in handy for table
|
|
|
- headers you want to stay on one line.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Floats and Clears
|
|
|
------------------
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-float-left
|
|
|
- floats left
|
|
|
-float-right
|
|
|
- floats right
|
|
|
-clear
|
|
|
- clears all
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Object Tools
|
|
|
-============
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Certain actions which apply directly to an object are used in form and
|
|
|
-changelist pages. These appear in a "toolbar" row above the form or changelist,
|
|
|
-to the right of the page. The tools are wrapped in a ``ul`` with the class
|
|
|
-``object-tools``. There are two custom tool types which can be defined with an
|
|
|
-additional class on the ``a`` for that tool. These are ``.addlink`` and
|
|
|
-``.viewsitelink``.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Example from a changelist page:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. code-block:: html+django
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- <ul class="object-tools">
|
|
|
- <li><a href="/stories/add/" class="addlink">Add redirect</a></li>
|
|
|
- </ul>
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. image:: _images/objecttools_01.png
|
|
|
- :alt: Object tools on a changelist page
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-and from a form page:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. code-block:: html+django
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- <ul class="object-tools">
|
|
|
- <li><a href="/history/303/152383/">History</a></li>
|
|
|
- <li><a href="/r/303/152383/" class="viewsitelink">View on site</a></li>
|
|
|
- </ul>
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. image:: _images/objecttools_02.png
|
|
|
- :alt: Object tools on a form page
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Form Styles
|
|
|
-===========
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Fieldsets
|
|
|
----------
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Admin forms are broken up into groups by ``fieldset`` elements. Each form fieldset
|
|
|
-should have a class ``.module``. Each fieldset should have a header ``h2`` within the
|
|
|
-fieldset at the top (except the first group in the form, and in some cases where the
|
|
|
-group of fields doesn't have a logical label).
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Each fieldset can also take extra classes in addition to ``.module`` to apply
|
|
|
-appropriate formatting to the group of fields.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.aligned
|
|
|
- This will align the labels and inputs side by side on the same line.
|
|
|
-.wide
|
|
|
- Used in combination with ``.aligned`` to widen the space available for the
|
|
|
- labels.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Form Rows
|
|
|
----------
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
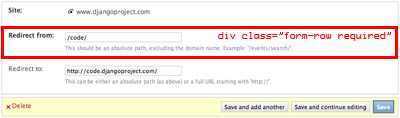
-Each row of the form (within the ``fieldset``) should be enclosed in a ``div``
|
|
|
-with class ``form-row``. If the field in the row is required, a class of
|
|
|
-``required`` should also be added to the ``div.form-row``.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-.. image:: _images/formrow.png
|
|
|
- :alt: Example use of form-row class
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Labels
|
|
|
-------
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Form labels should always precede the field, except in the case
|
|
|
-of checkboxes and radio buttons, where the ``input`` should come first. Any
|
|
|
-explanation or help text should follow the ``label`` in a ``p`` with class
|
|
|
-``.help``.
|